Water resource management (Jinsha, China)
Jinsha River Basin (JRB): Integrated Water Resources and Risk Management under Changing Climate
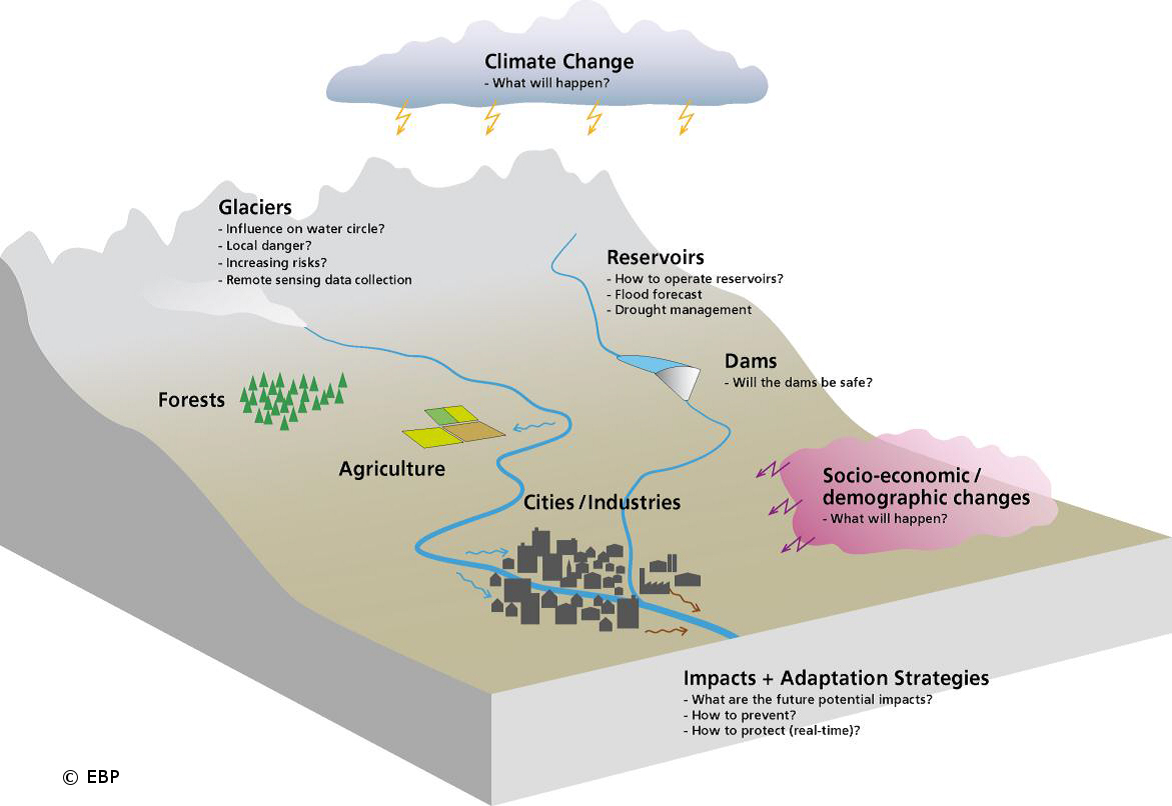
The aim of the “Jinsha River Basin (JRB): Integrated Water Resources and Risk Management under Changing Climate” project was to develop an integrated water resources and risk management system for the Jinsha river watershed in the context of climate change. The project has multiple aspects, since it aims to use an environmental approach to protect people and property from bad weather, while ensuring the viable development of the regional economy, and to stimulate discussion around the issue of global climate change.
The Jinsha watershed is located upstream of the Changjiang River (also known as the Yangtze), and plays an essential role in water resource management and hydropower production. The extent of the damage caused by the severe weather events to which this region has been subjected in recent decades has prompted the Chinese government to take an interest in the impacts of climate change, and to become involved in this multi-disciplinary collaborative project. The size of the study basin (473,200 km2, i.e. almost 12 times the surface area of Switzerland), its potential for energy exploitation (121,020 MW of hydroelectric power, of which 119,650 MW is technologically exploitable), and the strong socio-economic and environmental interdependencies that exist, enable us to grasp the importance of the project and envisage the scope of its results.
Financed by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation(SDC), this project is the result of a partnership between various public institutions and private Swiss and Chinese companies: on the Swiss side, the firms Ernst Basler + Partner(EBP), GEOTEST, Hydrique Ingénieurs and CREALP; and on the Chinese side, the Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute(CRSRI), the Bureau of Hydrology(BOH), the Changjiang Institute of Survey, Planning, Design and Research(CISPDR), the Institute of Hydro Ecology(IHE) and the Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute(NHRI). Further information is available on the official project page(SDC).
CREALP’s role in this large-scale project was to develop hydro-meteorological data analysis tools. These were then implemented in a hydrological model, with the aim of establishing medium- and long-term future scenarios, and thus understanding protection strategies adapted to this complex hydro-climatic problem.
Information
Contact: Bastien Roquier
Project duration: 2015 – 2018
Project sponsor: Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation(SDC)

